Spray Foam Insulation R-Value: What You MUST Know [2025 Complete Guide]
If you’re researching insulation for your home or building project, you’ve probably encountered the term “R-value” dozens of times. But here’s what most articles won’t tell you: R-value alone doesn’t determine how well your insulation actually performs in the real world.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about spray foam insulation R-values, from basic per-inch ratings to the surprising truth about why R-value isn’t the whole story.
Spray Foam R-Value Quick Facts
What is R-Value and Why Does It Really Matter?
The Simple Definition
R-value is a measure of thermal resistance — essentially, how well an insulating material resists the flow of heat. The higher the R-value, the better the material insulates.
Think of R-value like a traffic speed bump for heat. A higher R-value creates a bigger obstacle, slowing heat transfer more effectively.
What R-Value Measures (And What It Doesn’t)
Here’s where things get interesting — and where many homeowners get misled. R-value testing measures only conductive heat transfer through a material under controlled laboratory conditions. The standard tests assume:
- Zero air movement
- Zero moisture
- Perfectly still conditions
In reality, your walls experience wind, humidity, and air leakage. The U.S. Department of Energy notes that R-value depends on temperature, aging, and moisture accumulation in real-world applications.
Key Insight
This explains why spray foam often dramatically outperforms fiberglass at “equal” R-values. While fiberglass allows air to pass through (carrying heat with it), spray foam creates an air-tight barrier that stops both conductive AND convective heat transfer.
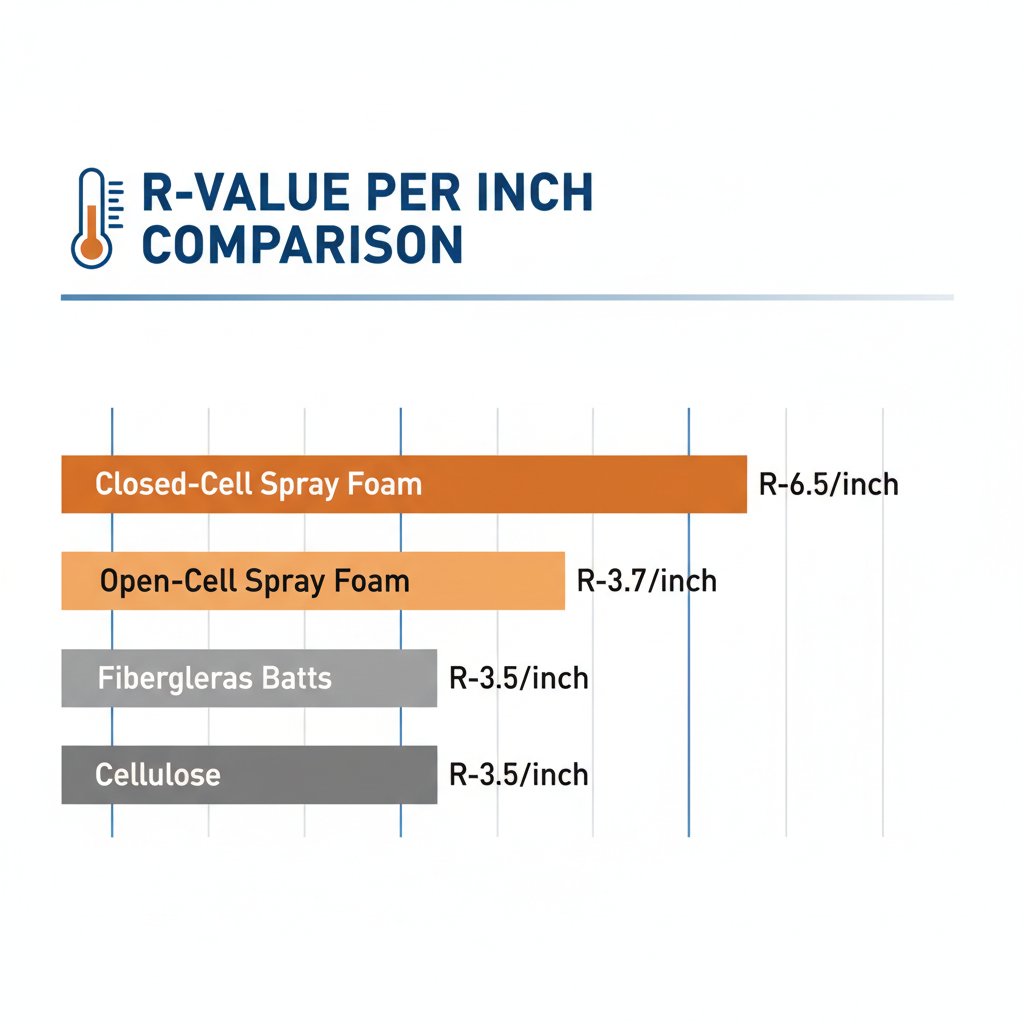
Spray Foam R-Value Per Inch: The Complete Breakdown
R-Value Comparison Chart
| Insulation Type | R-Value Per Inch | 3” Total | 6” Total | Air Barrier? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Closed-Cell Spray Foam | R-6.0 to R-7.0 | R-18 to R-21 | R-36 to R-42 | Yes |
| Open-Cell Spray Foam | R-3.5 to R-3.9 | R-10.5 to R-11.7 | R-21 to R-23.4 | Yes |
| Fiberglass Batts | R-3.2 to R-3.8 | R-9.6 to R-11.4 | R-19.2 to R-22.8 | No |
| Cellulose | R-3.2 to R-3.8 | R-9.6 to R-11.4 | R-19.2 to R-22.8 | No |
| Mineral Wool | R-3.0 to R-3.3 | R-9 to R-9.9 | R-18 to R-19.8 | No |
Closed-Cell Spray Foam: R-6.0 to R-7.9 Per Inch
Building Science Corporation specifies that high-density closed-cell spray foam (2.0 lb/cubic foot) provides R-5.5 to R-6.5 per inch for aged R-value. However, premium third-generation HFO formulations like UPC 2.0 HFO High Lift achieve R-7.9 per inch — among the highest available.
Foamology Uses Premium R-7.9 Foam
At Foamology Insulation, we use UPC 2.0 HFO High Lift closed-cell spray foam, which delivers R-7.9 per inch — approximately 13-20% higher than standard closed-cell products. This means you need less material to achieve the same insulation levels, and the HFO blowing agent has an ultra-low Global Warming Potential (GWP of 1).
Closed-cell advantages beyond R-value:
- Vapor barrier properties: At 2+ inches, it acts as a Class II vapor retarder
- Structural enhancement: Studies show 70-200% increase in wall racking strength
- Moisture resistance: The closed-cell structure doesn’t absorb water
- Maximum insulation in limited space: Ideal when cavity depth is restricted
Open-Cell Spray Foam: R-3.5 to R-3.9 Per Inch
Open-cell spray foam has a lower density (0.4-0.5 lb/cubic foot) and provides R-3.6 per inch. While the R-value per inch is lower than closed-cell, open-cell offers distinct advantages:
- Excellent soundproofing: STC ratings of 38-50, better than closed-cell (36-39)
- Vapor permeability: Allows moisture to dry through the foam
- Leak detection: In roof applications, you can spot leaks before they cause structural damage
- Cost-effective: Typically 30-40% less expensive than closed-cell
Open-Cell vs Closed-Cell R-Value Comparison
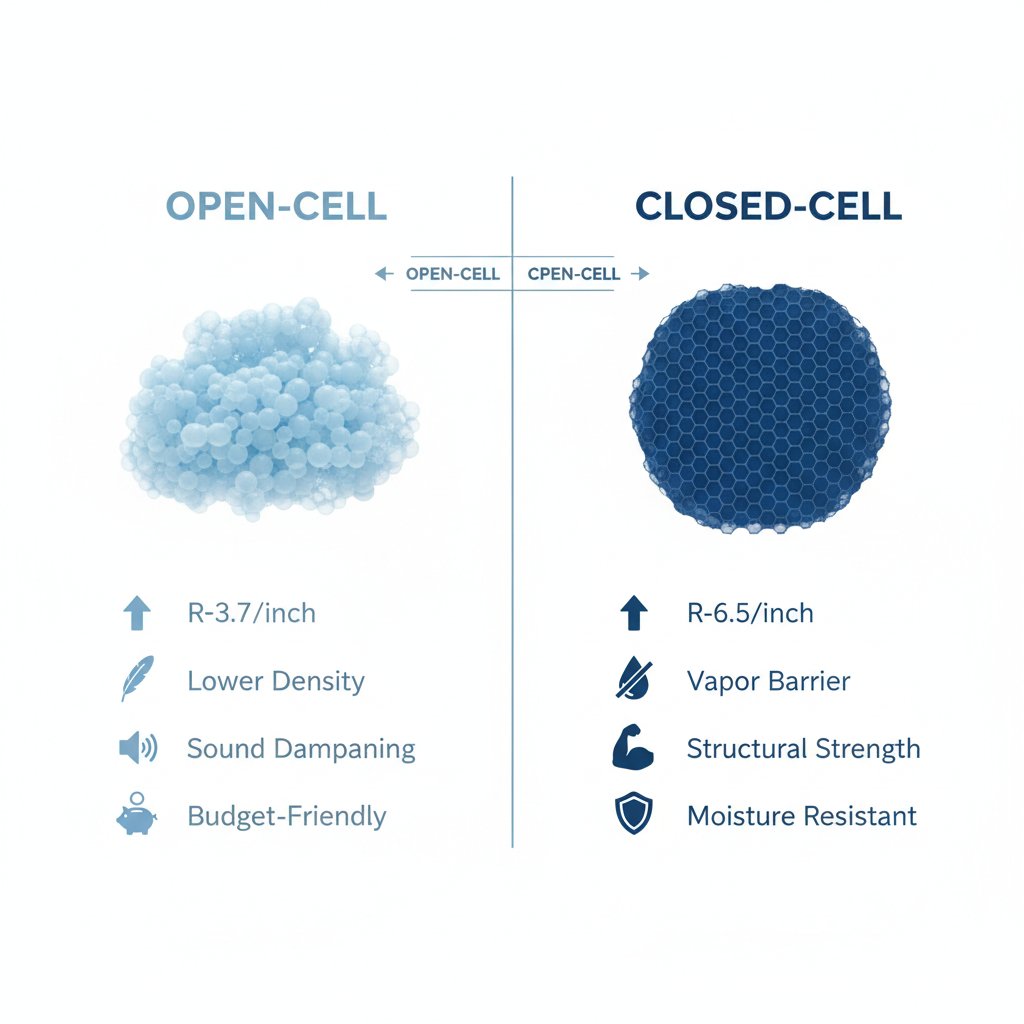
Complete Comparison Table
| Factor | Open-Cell | Closed-Cell |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value Per Inch | R-3.5 to R-3.9 | R-6.0 to R-7.0 |
| Density | 0.4-0.5 lb/ft³ | 1.5-2.2 lb/ft³ |
| Vapor Barrier | No (vapor permeable) | Yes (at 2+ inches) |
| Air Barrier | Yes (at 3+ inches) | Yes (at 2+ inches) |
| Sound Dampening | Excellent (STC 38-50) | Good (STC 36-39) |
| Moisture Resistance | Absorbs/releases moisture | Waterproof |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Applications | Interior, attics, sound walls | Exterior, basements, roofs |
When R-Value Isn’t the Deciding Factor
Both open-cell and closed-cell spray foam create effective air seals. Since air leakage accounts for 30-40% of energy loss in typical homes, this air-sealing capability often matters more than the difference in R-value.
According to Fine Homebuilding, “What really matters is the R-value of the whole wall, not just that of the insulation.”
R-Value Requirements by Climate Zone (2025 IECC Codes)
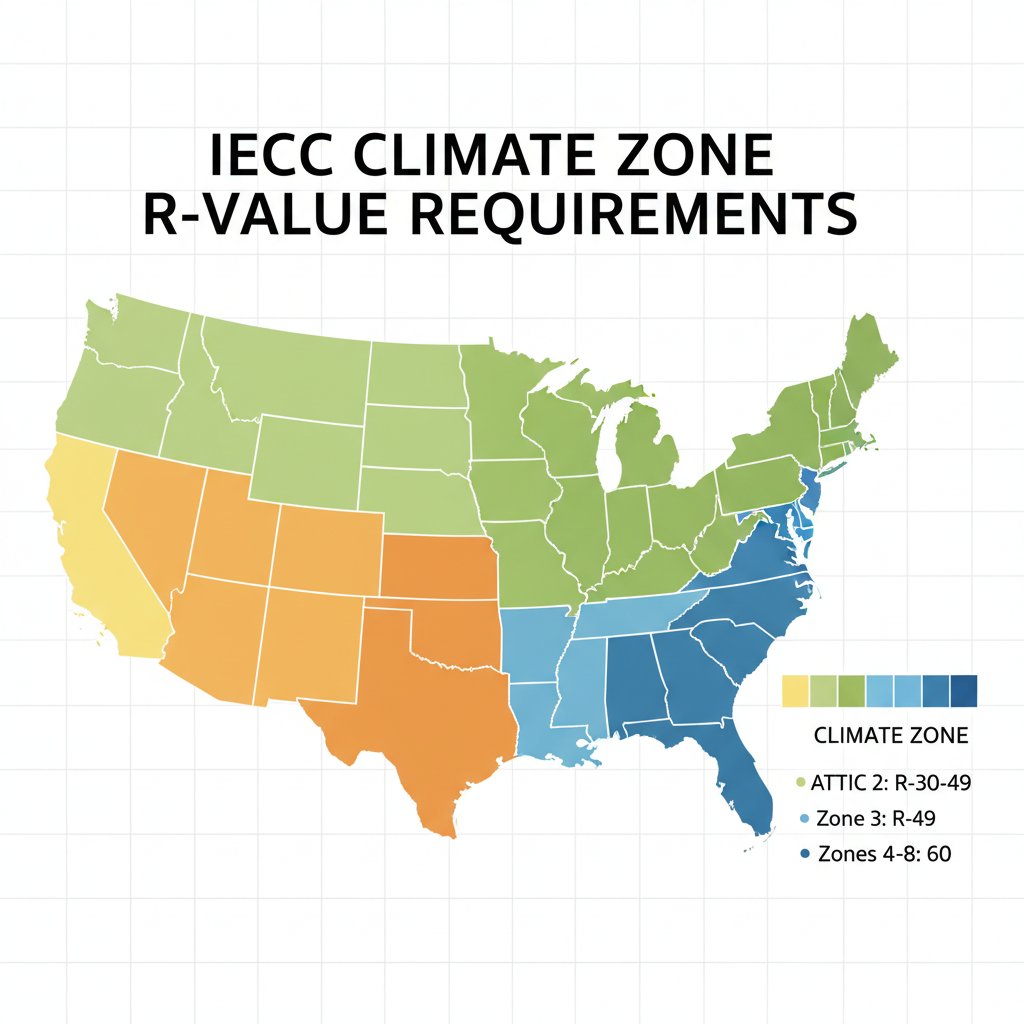
Climate Zone R-Value Requirements
| Climate Zone | Ceiling R-Value | Wall R-Value | Floor R-Value | Basement Wall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zone 1 | R-30 | R-13 | R-13 | None required |
| Zone 2 | R-49 | R-13 | R-13 | None required |
| Zone 3 | R-49 | R-20 or R-13+5ci | R-19 | R-5ci |
| Zone 4 | R-60 | R-20+5ci or R-13+10ci | R-19 | R-10ci |
| Zone 5-6 | R-60 | R-20+5ci or R-13+10ci | R-30 | R-15ci |
| Zone 7-8 | R-60 | R-20+5ci or R-13+10ci | R-38 | R-15ci |
Note: “ci” indicates continuous insulation on exterior
How to Calculate Required Spray Foam Thickness

Basic Calculation Formula
Required Thickness = Target R-Value ÷ R-Value Per Inch
Calculation Examples
Example 1: Achieving R-30 in an Attic
- Using closed-cell (R-6.5 per inch): R-30 ÷ 6.5 = 4.6 inches
- Using open-cell (R-3.7 per inch): R-30 ÷ 3.7 = 8.1 inches
Example 2: Achieving R-49 in an Attic
- Using closed-cell (R-6.5 per inch): R-49 ÷ 6.5 = 7.5 inches
- Using open-cell (R-3.7 per inch): R-49 ÷ 3.7 = 13.2 inches
Example 3: Flash-and-Batt Hybrid for R-49
- 2 inches closed-cell spray foam = R-13
- R-36 fiberglass batts = R-36
- Total: R-49
Why R-Value Isn’t the Whole Story
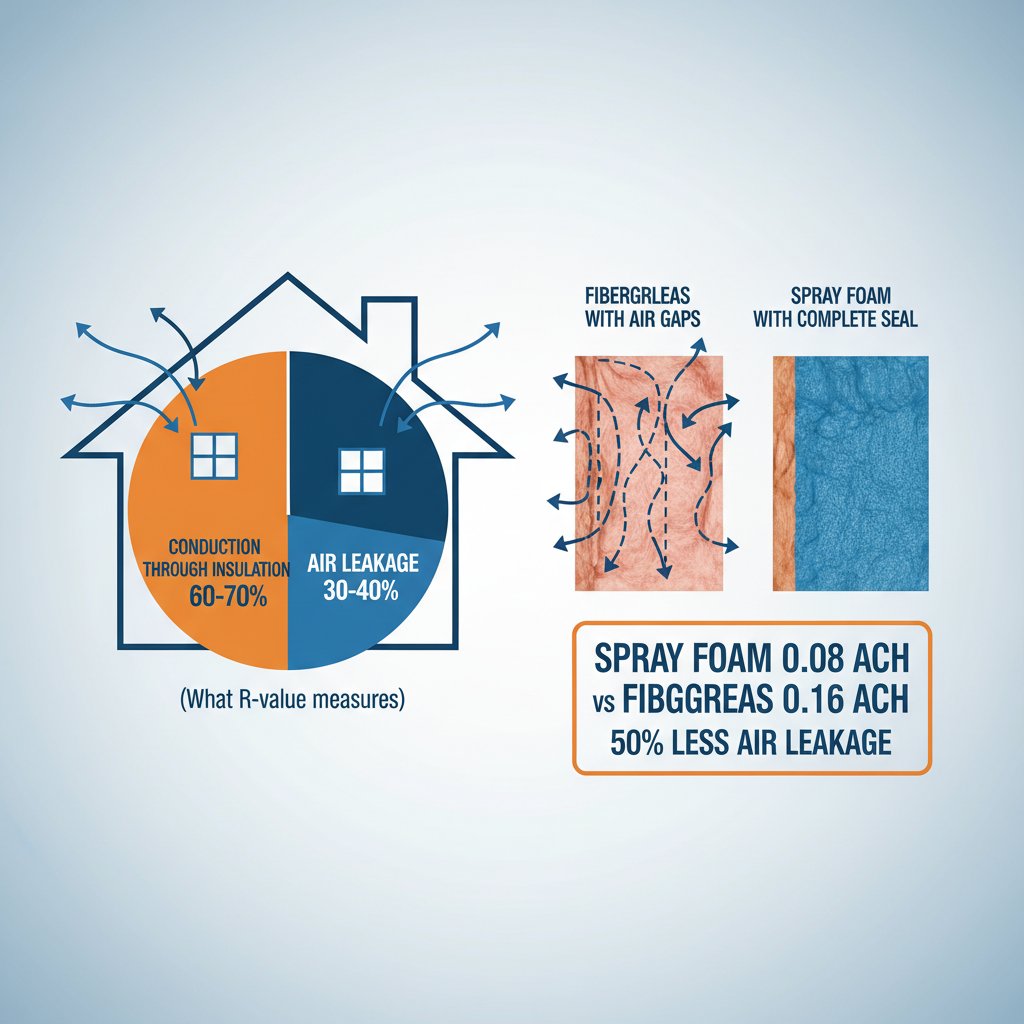
The Air Sealing Advantage
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, 30-40% of the energy lost in a typical home escapes through air leakage — not through the insulation itself. This means that stopping air infiltration can be as important as (or more important than) adding R-value.
Spray foam creates a monolithic air barrier that traditional insulation simply cannot match. Research from Oak Ridge National Laboratory demonstrated this dramatically:
Air Leakage Comparison
Thermal Bridging: The Hidden R-Value Killer
Even perfect cavity insulation faces thermal bridging through framing members. Wood has an R-value of only about R-1.2 per inch. Since framing typically accounts for 25% of wall area, significant heat transfer occurs right through the studs.
Building Science Corporation research shows:
- A wall with R-30 cavity insulation might have only R-16 to R-20 whole-wall R-value
- This 30-40% reduction affects all insulation types equally
Spray Foam vs Fiberglass R-Value Comparison
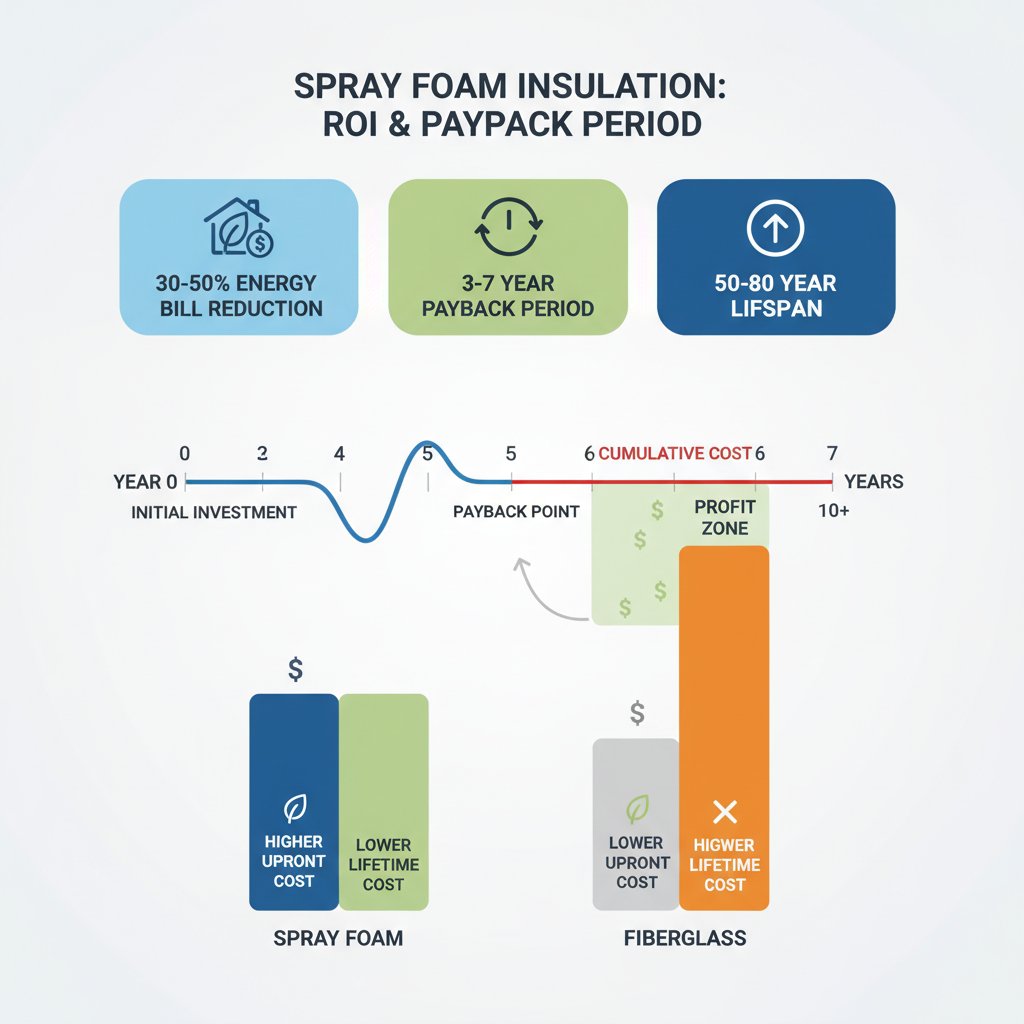
| Factor | Spray Foam | Fiberglass Batts |
|---|---|---|
| R-Value Per Inch | R-3.5 to R-7.0 | R-3.2 to R-3.8 |
| Air Sealing | Complete barrier | None |
| Installation Quality | Consistent | Variable - gaps common |
| Lifespan | 50-80 years | 10-25 years |
| Energy Savings | 30-50% | 20-30% |
Is Higher R-Value Always Better? Understanding Diminishing Returns
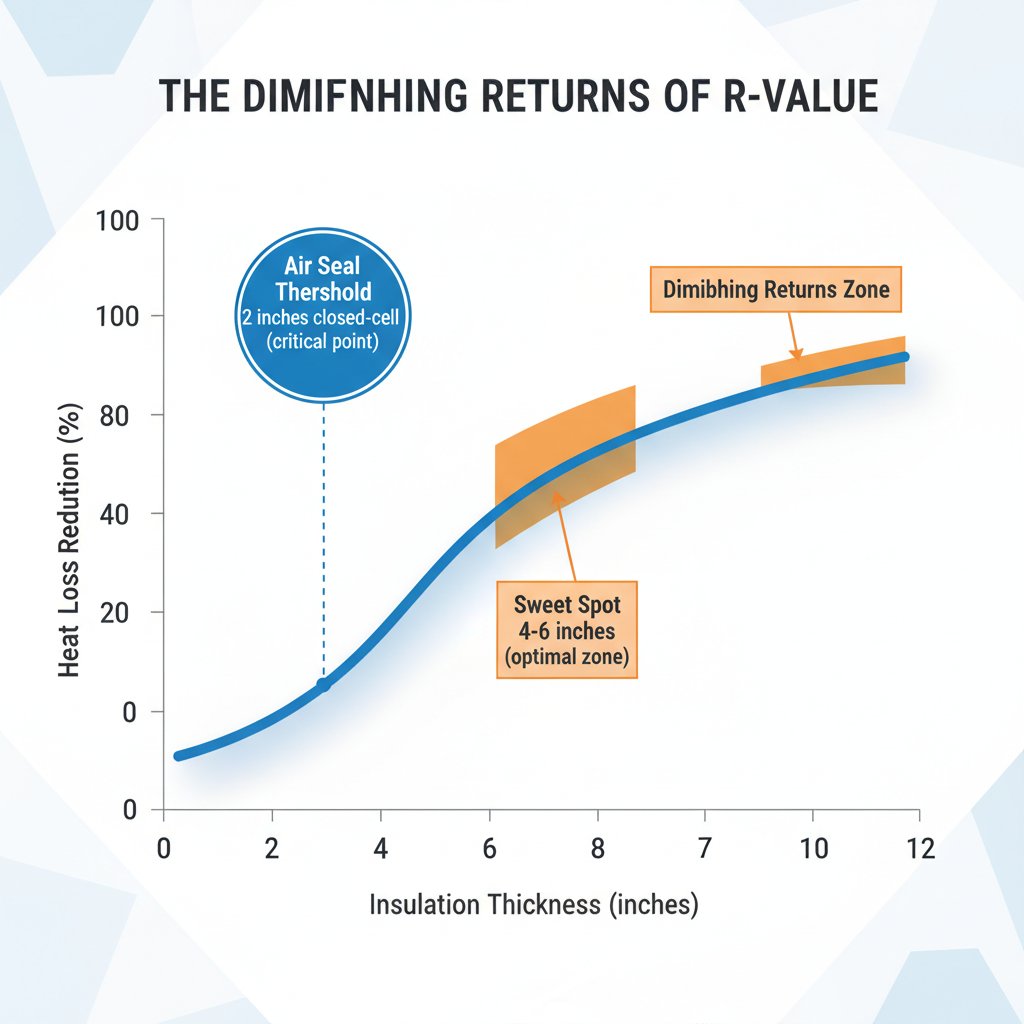
The Concept of Diminishing Returns
Each additional inch of insulation provides less incremental benefit than the previous inch:
- From R-0 to R-10: Reduces heat loss by 90%
- From R-10 to R-20: Reduces remaining heat loss by 50% (5% total improvement)
- From R-20 to R-40: Reduces remaining heat loss by 50% (2.5% total improvement)
Where the Critical Thresholds Are
Critical Thresholds
Air Seal Threshold (most critical):
- Closed-cell: 2 inches minimum
- Open-cell: 3 inches minimum
Sweet Spot Range: 3-6 inches of closed-cell for most applications
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the R-value of spray foam per inch?
Closed-cell spray foam provides R-6.0 to R-7.0 per inch (aged R-value), while open-cell spray foam provides R-3.5 to R-3.9 per inch.
Which has higher R-value: open-cell or closed-cell?
Closed-cell spray foam has nearly double the R-value per inch (R-6 to R-7) compared to open-cell (R-3.5 to R-3.9). However, both provide effective air sealing, so the real-world performance difference is often smaller than the numbers suggest.
How thick should spray foam be in an attic?
Attic thickness depends on your climate zone. To meet 2021 IECC requirements of R-49 to R-60: Closed-cell needs 7.5 to 10 inches, Open-cell needs 13 to 17 inches, or a Flash-and-batt hybrid with 2” closed-cell plus R-36-47 fiberglass.
Does spray foam lose R-value over time?
Minimal loss occurs — a fraction of a percent over the life of the insulation. The R-values advertised by manufacturers are “aged” values that already account for initial thermal drift. Spray foam maintains its performance for 50-80 years.
Is higher R-value always better?
Not necessarily. Beyond the minimum thickness for air sealing (2” closed-cell, 3” open-cell), you reach diminishing returns. Air sealing typically provides more energy benefit than additional R-value in most applications.
What R-value do I need for my climate zone?
Requirements range from R-30 (warm climates, Zone 1) to R-60+ (cold climates, Zones 4-8) for attic insulation, and R-13 to R-20+ for walls. Check the 2021 IECC requirements for your specific climate zone.
How does spray foam R-value compare to fiberglass?
Spray foam provides R-3.5 to R-7.0 per inch versus fiberglass at R-3.2 to R-3.8 per inch. More importantly, spray foam also provides complete air sealing, which fiberglass cannot.
Is spray foam worth the higher cost?
For most applications, yes. Energy savings of 30-50% (compared to 20-30% for fiberglass) typically provide a 3-7 year payback. Spray foam also lasts 50-80 years compared to 10-25 years for fiberglass.
Ready to Learn More About Spray Foam for Your Project?
Get a professional R-value assessment and custom recommendations for your home based on your climate zone and energy goals.
For professional spray foam installation that meets or exceeds your climate zone requirements, contact Foamology Insulation. Our experienced team can assess your specific situation and recommend the optimal solution for your home.